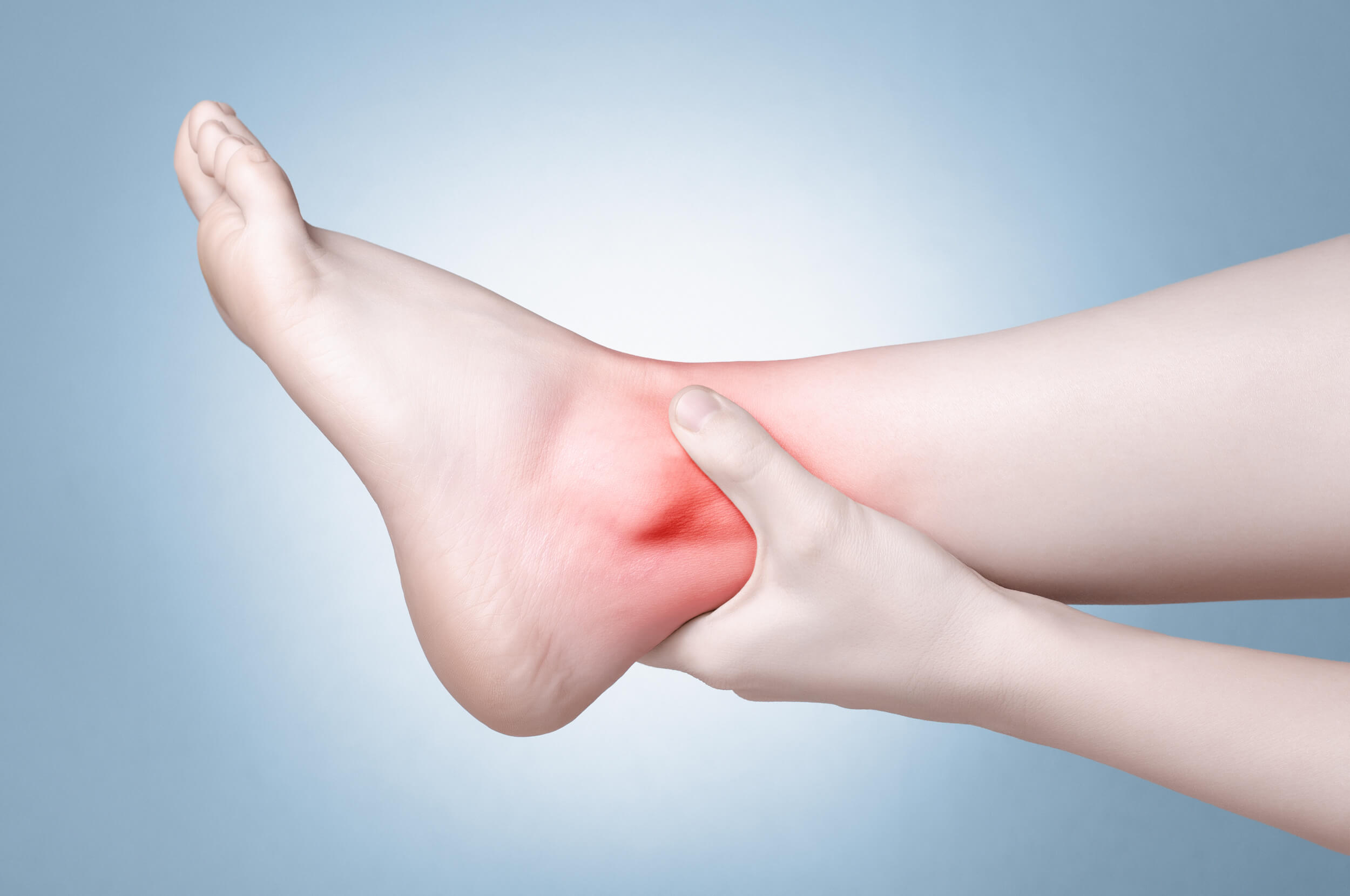
Foot Sprain vs. Strain
A foot sprain and a foot strain are two common injuries many receive in their lifetime. They frequently happen to those with active lifestyles, such as athletes, although they can also be experienced by anyone who can walk and run. Despite being non-threatening, sprains and strains are still painful and disruptive to daily activities. Hence, it’s a must to treat them immediately to avoid complications.
But these two injuries are often interchanged and confused with each other. They’re alike in terms of injury area and symptoms. So, figuring out the correct care methods is tricky if you don’t know what you have exactly.
This article is your in-depth guide on recognizing foot sprains and strains. After reading, you should understand their causes and know how to treat them accordingly.
Key Differences
Foot sprains and strains usually occur around the ankles and sometimes the back of the legs, known as the hamstrings. Pain from either injury also feels similar to each other. Professional podiatrists, like those from Teton Foot and Ankle, can diagnose your condition and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Their differences lie in the actual source of the pain. Simply put, foot strains are tears on the tendons and muscles. Tendons connect your muscles to your bones. They can be partial or complete muscle tears that can manifest as spasms, cramping, swelling, weakness, or inflammation.
Meanwhile, sprains are overstretched foot ligaments or the tissues that connect two bones. Depending on the severity, you can also categorize foot sprains into three types, which are:
- Grade I (minor) – Light tears, stretching, or mild damage to fibers in your ligaments
- Grade II (moderate) – Larger tears and looseness in the affected joint when moved in certain angles
- Grade III (severe) – Completely detached or torn ligament that may make the foot unstable
Whether the pain is mild or not, it’s best to call a doctor immediately. If you’re the one injured, refrain from moving too much and wait until medical professionals arrive.
Common Causes
Sudden twists, impacts, and falls are the common causes of foot sprains and strains. Thus, it’s why they can happen to both athletic and non-athletic individuals. You could get either injury if you land incorrectly after jumping or pivot your foot the wrong way while running. Sometimes, even tripping on a rock or elevated surface might cause the joint to tear slightly.
Overuse of a particular joint, such as your ankles, may also cause these two injuries. In addition, some physical activities may require repetitive movements, resulting in tears in your tendons, muscles, or ligaments without proper rest.
After an injury, contact a medical professional before the condition worsens. It could be a strain or a sprain, but it’s possible it could be a fracture or a plantar fasciitis upon further inspection. The latter two more severe issues also share similar initial symptoms with foot sprains and strains until you feel a sharp pain.
Treatment And Care
The RICE technique is the most widely-used treatment for acute soft-tissue injuries like foot sprains and strains. Each letter stands for a step in that method, which are the following:
- Rest. The individual must immediately pause the physical activity that caused their injury. Depending on the situation, let them sit or lie down to rest their affected limb.
- Ice. Pour ice cubes into a plastic bag or, if unavailable, use a sealed pack of frozen vegetables. A damp towel inside a resealable bag will also do after you’ve put it in the freezer for a minimum of 15 minutes. Place the cold compress on the affected area and leave it on for around 20 minutes several times a day.
- Compression. Wrap an elastic bandage around the affected joint to reduce swelling. Avoid wrapping it too tight that it may restrict blood circulation. A doctor may also recommend a special boot or cast to prohibit excessive movement.
- Elevation. Raise the injured limb above heart level, at least six inches higher. Doing this will also reduce swelling. You can use a pillow or layered blankets as elevation for your foot.
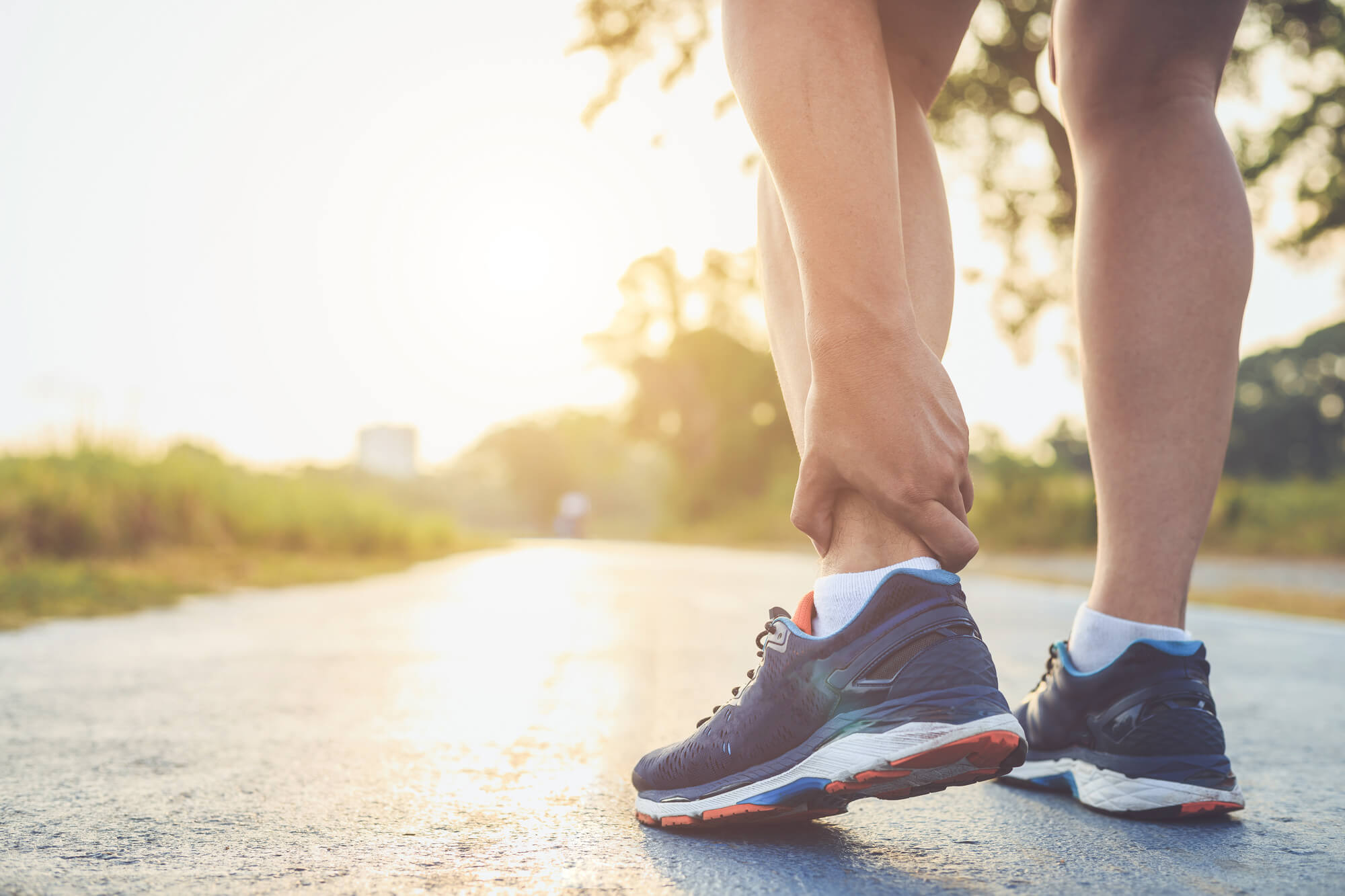

Foot Sprain vs. Strain
You can easily do the RICE method at home to treat foot strains and sprains. But keep in mind your doctor’s advice for further treatment. If you’re an athlete, your healthcare provider might suggest wearing a custom orthotic to improve your performance and reduce the risk of further injury. Either way, you must continue to perform the RICE treatment until your doctor says otherwise.
You may be prescribed over-the-counter painkillers or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Acetaminophen is another medication to curb the pain. Your healthcare provider might also suggest you find a physical therapist regardless of your injury’s severity. Therapy will aid in increasing your strength and improving mobility after healing. For more severe conditions, surgery is needed to repair damaged tissues.
Recovery Period
Foot strains and minor to moderate foot sprains generally heal independently after a few days to a couple of weeks. A Grade I sprain could take two to four weeks. With a splint on, a Grade II sprain may heal within eight weeks. However, expect full mobility after at least eight months for Grade II sprains.
Prevention Methods
To avoid a foot strain or sprain from happening, make sure you wear the proper shoes for a specific activity. Footwear designed to protect your feet and provide ample comfort can prevent a possible injury. Refrain from using loose, open-toed shoes or sandals when running or doing high-intensity sports. Additionally, watch where you’re walking to avoid obstacles that may hurt you.
Building your flexibility will benefit you whether you’re an athlete or not. Rotating and stretching your feet before a walk or doing sports warms up and loosens tight muscles. You must also strive to maintain a healthy weight. Heavier bodies tend to put more pressure and stress on the feet, making them prone to injury.
When you’ve recuperated from a previous foot sprain or strain, avoid hurting it again. Repeated pressure on the same area may result in worse injuries since that body part requires time to heal fully. So, limit your movements as much as possible or per your healthcare provider’s advice.
Conclusion
Foot strains and sprains are similar except for the location of the damage. Strains are tears in the tendon and muscle, while sprains are tears in the ligaments. Causes and treatment are also the same but may differ depending on severity.
Whichever you happen to have, remember to keep calm and refrain from moving your injured foot. Prompt treatment, an excellent podiatrist, and therapy will help you walk on your path to recovery.