Functions of Public Health Professionals
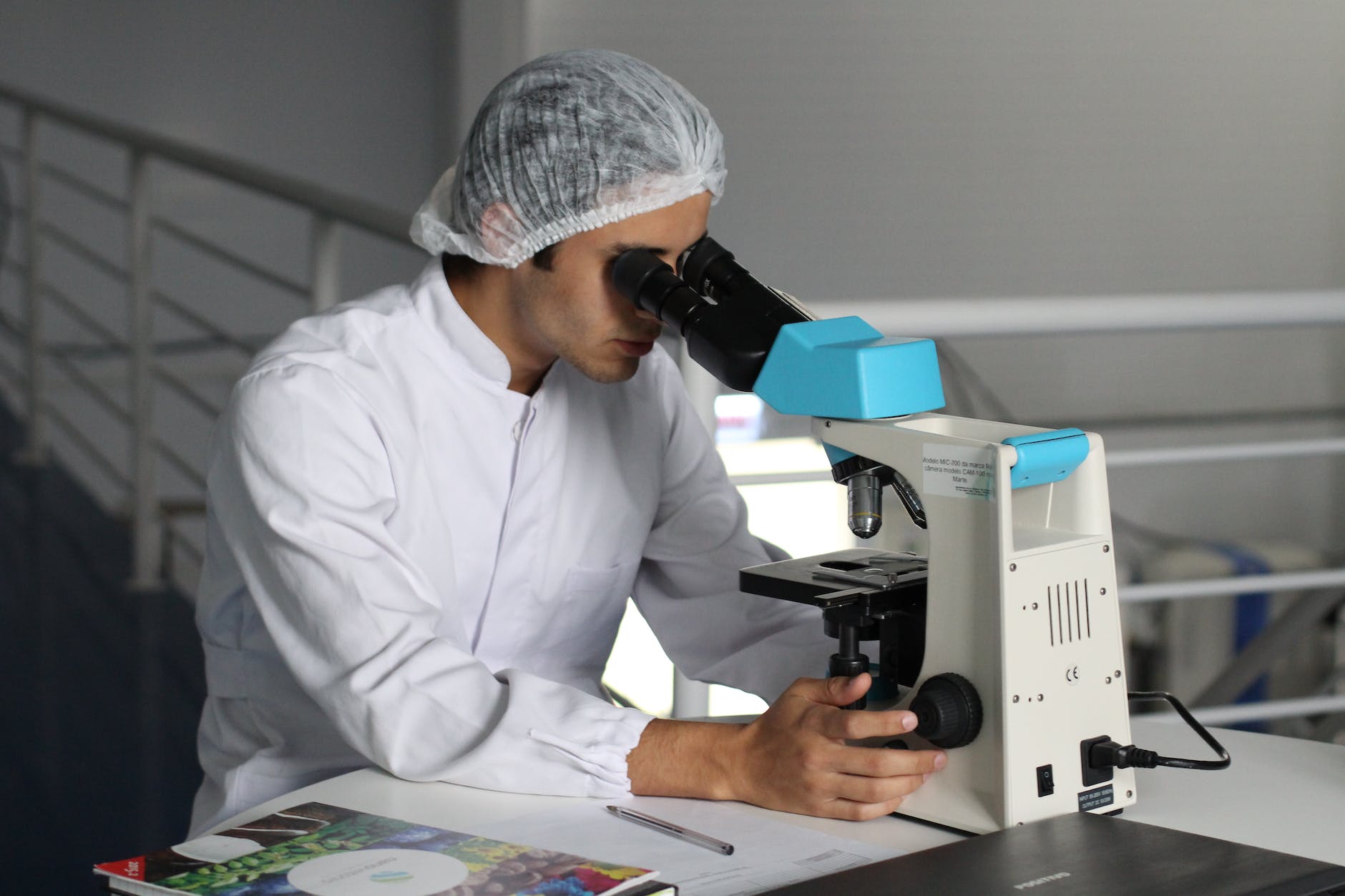
Public health professionals play a crucial role in promoting and protecting the health of communities. They address a wide range of health issues and promote well-being at a population level. From disease surveillance and outbreak investigation to health promotion and community engagement, public health professionals are equipped with the knowledge and skills to tackle some of society’s most pressing health challenges.
This article will explore public health professionals’ most important functions and how they improve communities’ health and well-being. From implementing health policies and conducting research to managing healthcare systems and responding to emergencies, we will provide a comprehensive overview of public health professionals’ roles.
Health promotion and disease prevention
Health promotion and disease prevention are essential aspects of public health aimed at improving health and preventing the onset and progression of the disease. These are the basics of every advanced public health program that prepares them to tackle real-world problems. Professionals in these programs get the skills and knowledge needed to design and implement effective programs and policies. These programs may include education, outreach initiatives, and environmental and policy interventions. For example, health promotion activities may target behavior change to encourage healthy habits, such as regular physical activity and healthy eating. Disease prevention may involve implementing screening programs, providing access to vaccines, or controlling the spread of infectious diseases.
Public health professionals looking to grow in their careers and better understand these functions can enroll in accredited MPH online programs.
Epidemiology
Epidemiology is a crucial field of public health that studies the distribution and determinants of health and disease in populations. Epidemiology aims to understand the factors contributing to populations’ health and to develop strategies for preventing and controlling infections. Epidemiologists use data to identify patterns, causes, and risk factors for diseases and evaluate public health interventions’ effectiveness. Epidemiologists use various research methods to gather and analyze data. These methods include observational studies, clinical trials, and mathematical modeling. The insights gained from epidemiologic research are used to inform public health policies and programs and to improve health outcomes for individuals and communities.
Environmental Health
Environmental health is a branch of public health that focuses on the impact of the environment on human health. It involves identifying and addressing environmental factors that contribute to disease and injury. Environmental health professionals work to prevent exposure to environmental hazards, such as air and water pollution, hazardous waste, and toxic substances. They also improve access to safe and healthy housing and promote healthy communities through land use planning and transportation policies. The field also encompasses food safety, disaster preparedness and response, and climate change and its impact on health. Environmental health professionals use various tools and approaches to understand and mitigate the health effects of environmental exposures. Protecting public health through a healthy environment is a critical goal of environmental health professionals.
Emergency Preparedness
Emergency preparedness is a critical aspect of public health that involves planning, organizing, and preparing for potential public health emergencies. It encompasses a range of activities, from risk assessment and hazard identification to developing plans and protocols for a response. Effective emergency preparedness requires coordination and collaboration among multiple organizations and stakeholders, including government agencies, healthcare providers, and community-based organizations. The goal of emergency preparedness is to reduce the impact of disasters on public health and ensure a rapid and effective response to minimize harm. It involves preparing for potential emergencies, including natural disasters, pandemics, and bioterrorism incidents.
Health Policy Development
Health policy development is creating and implementing policies to improve health outcomes and address public health issues. It involves the identification of priority health problems, the development of evidence-based solutions, and the creation of policies and programs to address these issues. Health policy development is a complex and dynamic process involving the participation of multiple stakeholders, including government agencies, healthcare providers, researchers, and community members. Effective health policy development requires a strong understanding of the social, economic, and political factors that influence health and a deep understanding of public health science. Health policy development aims to create effective, equitable, and sustainable policies that improve health outcomes for individuals and communities.
Health Services Research
Health services research is a field of study that focuses on the organization, delivery, financing, and use of healthcare services. It seeks to improve the quality and efficiency of healthcare delivery and to increase access to care. Health services researchers use large data sets, surveys, and case studies to understand how healthcare services are used. They also figure out how they affect health outcomes and how they can be improved. The findings of health services research inform the development of policies and programs that aim to improve healthcare delivery quality, access, and cost-effectiveness. Health services research also plays a crucial role in guiding the allocation of healthcare resources and improving healthcare delivery systems’ efficiency and effectiveness.
Clinical Services
Direct delivery of healthcare to patients is what clinical services are about. Diagnostic and treating illnesses are some activities included in clinical services. These services are provided by healthcare professionals, including physicians, nurses, and other healthcare providers, who work together to ensure that patients receive high-quality, evidence-based care. They can be delivered in various settings, including hospitals, clinics, and community-based health centers. Clinical services aim to improve patients’ health outcomes and ensure that all individuals have access to the care they need when they need it. Clinical services are an essential component of the healthcare system and play a critical role in promoting the health and well-being of individuals and communities.
Conclusion
Public health professionals play a crucial role in promoting and protecting the health and well-being of individuals and communities. They address many public health challenges, from preventing disease and injury to improving access to care and quality of life. Public health professionals are needed in government agencies, healthcare organizations, and community-based organizations. Public health professionals aim to improve health outcomes for individuals and communities and create a more equitable and sustainable healthcare system. By working together and using their experience, public health professionals have the power to create meaningful change and to make a positive impact on the health and well-being of individuals and communities.