Wearable Health Devices
Wearable devices can detect early signs of illness, allowing users to identify any issues with their health quickly. This enables proactive actions that minimize complications and reduce dependency on costly medical interventions.
Moreover, wearable technology can facilitate telehealth solutions, expanding healthcare services to remote patients. This will increase patient engagement and foster a stronger bond between doctors and patients.
Real-time Data Collection
One of the most significant ways wearables impact preventative medicine is through their continuous collection of personalized health data. By constantly monitoring vital signs, exercise levels, and sleep patterns, individuals can identify their unique needs and improve self-management decisions.
For example, suppose someone notices they need to get more sleep or feel more stressed than usual. In that case, the ability to monitor these changes can motivate them to make lifestyle adjustments and seek medical advice. On the other hand, if a wearable detects a person has fallen, it can automatically notify their circle of caregivers or 911 to provide immediate assistance.
Medical wearables also enable healthcare specialists to monitor patients remotely, reducing office visits and staff workload. They can also reduce readmission rates for patients released from the hospital, resulting in cost savings for both parties.
Communication with Healthcare Providers
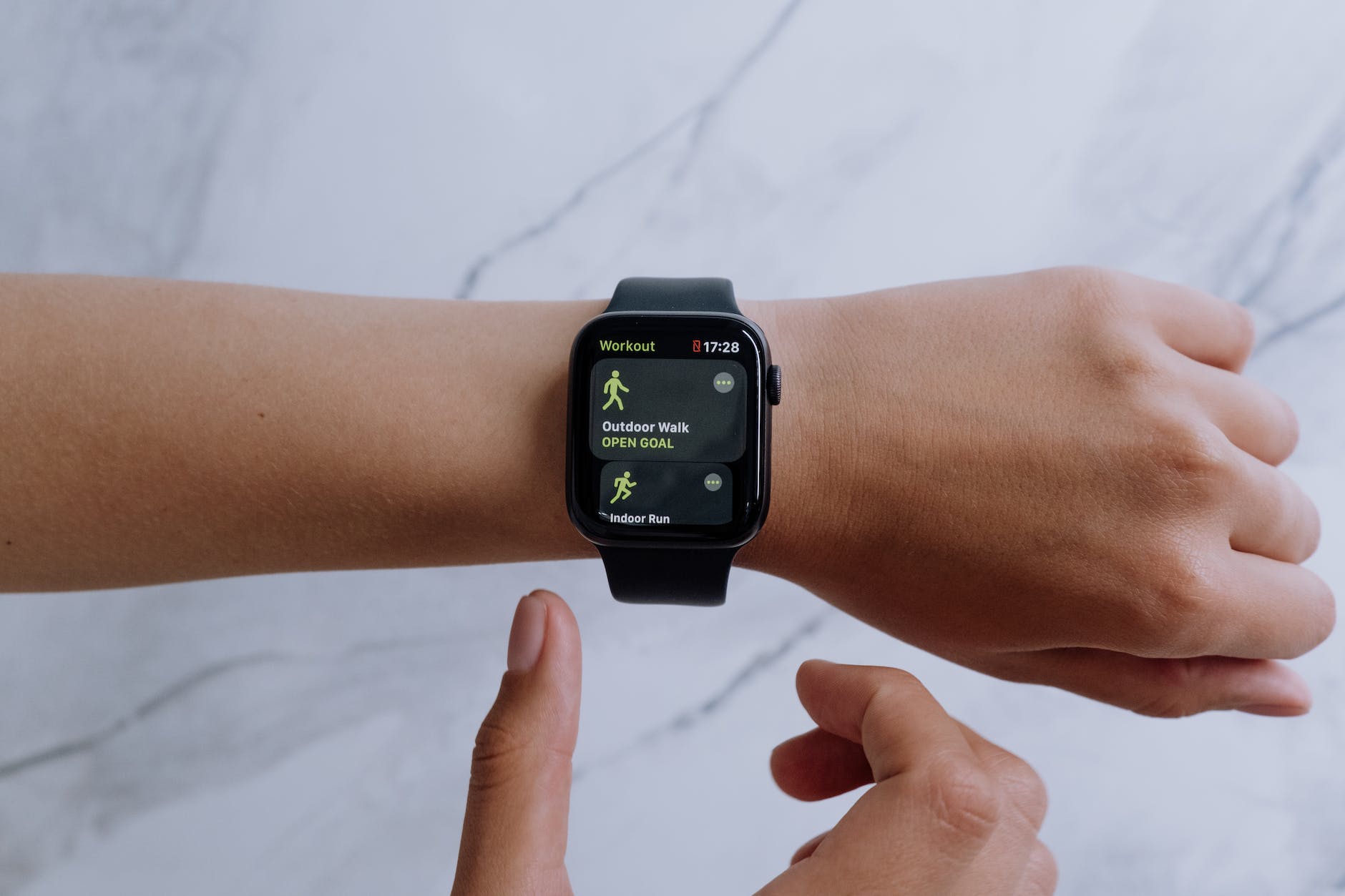
Wearable technology allows individuals to easily monitor their health, including heart rate, calories burned, and sleep patterns. Wearable health devices also provide alerts for potential problems such as high blood pressure or an elevated body temperature, allowing healthcare professionals to intervene quickly and prevent costly hospital stays.
Smart healthcare wearables are becoming increasingly popular in the world. These include fitness trackers, smartwatches, electrocardiogram (ECG) devices, blood pressure monitors, biosensors, and Wearable diagnostics. They can also monitor the body’s temperature, allowing individuals to spot the rise in body temperature that usually accompanies COVID-19 outbreaks.
Studies have found that several factors, including perceived benefits and value, usability, compatibility, aesthetics, and brand image, influence the continuous use intention of healthcare wearables. However, health improvement expectancy has been found to play the most critical role in determining users’ continual use intentions for these technologies. Healthcare wearables can give them a better sense of self-efficacy by facilitating healthy lifestyles.
Self-Management
When it comes to preventative healthcare, self-management is critical. Wearable devices encourage individuals to take responsibility for their health by providing real-time data and helping them track progress and set wellness goals. This sense of ownership can lead to a more proactive approach to self-care, ultimately improving healthcare outcomes and reducing reliance on medical services.
Moreover, many wearables have a user-friendly interface that makes it easy for users to access their health data and monitor their progress. This can motivate patients to stay engaged with their health and encourage them to continue following their treatment plans.
Wearable technology also enhances telehealth solutions, enabling physicians to monitor patient progress remotely and intervene promptly when needed. This can help reduce hospital readmissions, improve chronic disease management, and optimize overall healthcare system efficiency.
Prevention
Wearables are an innovative approach to healthcare that can help reduce the number of hospital visits, decrease staff workloads, and reduce overall costs. Medical specialists can identify potential health risks by monitoring patients remotely and take quick action if needed.
Medical wearables can also assist with prevention by helping patients adopt healthy habits that lead to healthier lives, such as meal planning, exercise, and sleeping. The wearables can offer just-in-time coaching and reminders to help form these new habits.
Several factors can influence usage behavior for healthcare wearable devices, including the perceived usefulness and ease of use. In addition, the study found that age, education, and income are associated with higher or lower wearable use by people with cardiovascular disease. To improve the use of wearables, manufacturers should focus on service innovation that adds value for consumers and incentivizes them to continue using their devices. The findings of the study help guide healthcare-related institutions and producers to create better healthcare-related wearables that increase user adoption.